There are different graphical Techniques, that still look very similar. because they are all built from so-called "Nodes" and "Edges".
- Nodes are Rectangles with a unique Name printed on them
- Edges are Linies or Arrows between these Nodes. They can be annotated with a brief Label.
Due to the graphical Representation, all Elements of a Thought can be grasped at a Glance. This considerably supports Understanding and Remembering. Missing Parts and Contradictions are easier to identify than e.g. in Texts. All Maps use the Principle of mental Association, to unfold Thoughts and to support the Brain.
They differ in Detail and Intention, with Spoc-Web having th emost expressive and Power by implementing a Super-Set of these Structures and more.
Mind Maps
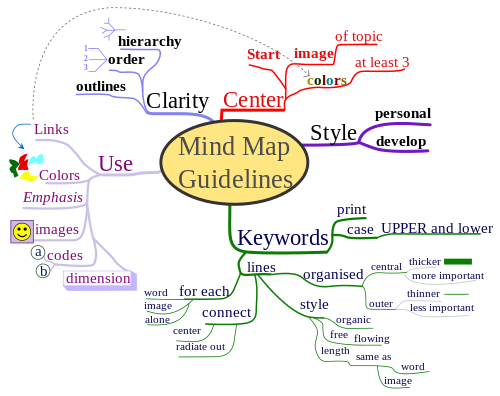
Mind Maps are a Technique introduced by Tony Buzan around 1970. It is primarily used for Introduction to and visual Representation of a single Idea, for Planning or for Notes. The Mind-Map is hierarchical and is built, starting from a central Topic. "Hierarchical" means that Connections are always directed "outward", going from more central Themes to periphereal ones. This has some Advantages:
- easy to grasp
- no "Cycles" allowed. Navigation through the Content is a simple "Tree-Walk"
- Nodes can be omitted and replaced by Labels on the Edges
At the same Time it is a big Disadvantage, because only simple radically simplified Comcepts can be represented.
Concept Maps
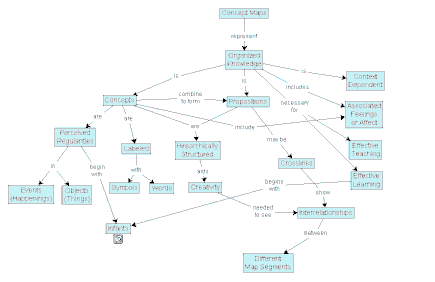
Concept Maps are not restricted in their Connections like Mind Maps. They are used to represent any Kind of Knowledge.
Studies show that Knowledge can be acquired faster and retained longer with Concept-Maps than with other Learning Methods. (Nesbit, J. C. , Adesope, O. O. (2006).
Learning with concept and knowledge maps: a meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 76, 413-448).
The graphical Representation allows Recognition even after long Time Periods. You can start working immediately on a known Concept Map without long Reading or Searching.
Unfortunately Computer Support is limited to Operations like Editing, Storage and Navigation.
(XML-) Topic Maps
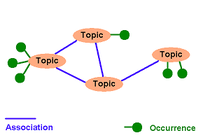
Topic Maps are an ISO-Standard (ISO/IEC 13250) to capture Knowledge. An XML-Data Format is also defined. Topic Maps primarily contain linguistic Elements like "Topics", "Associations" between Topics and "Occurrences" of Topics in Documents e. g. on the WWW. This facilitates Reseach and Translation of Knowledge.
Topic Maps are very close Siblings to semantic Webs, but not as widely known and harder to handle.
Semantic Webs
Semantic Webs are used to represent Knowledge, especially in Linguistics and Computer Science. Different from the Methods described above, these Webs are directly mapped to Data Structures. Graphical Display is not the primary Focus with semantic Webs.
Tim Berners-Lee, the Creator of the Internet (WWW) propagates the semantic Web since 2000. In represents both concrete as well as abstract Things with URIs. Things are connected with brief Sentences of three Elementes (RDF-Triplets): Subject, Predicate/Verb and Objekt. This universal Structure also allows to capture quantitative Data. This enables the Computer to offer considerable more powerful Support:
- Searching for Connections
- Filtering by Properties and Values
- even deriving new Knowledge from known Facts
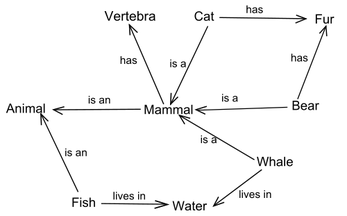
Semantic Webs are used to represent Knowledge, especially in Linguistics and Computer Science. Different from the Methods described above, these Webs are directly mapped to Data Structures. Graphical Display is not the primary Focus with semantic Webs.
Tim Berners-Lee, the Creator of the Internet (WWW) propagates the semantic Web since 2000. In represents both concrete as well as abstract Things with URIs. Things are connected with brief Sentences of three Elementes (RDF-Triplets): Subject, Predicate/Verb and Objekt. This universal Structure also allows to capture quantitative Data. This enables the Computer to offer considerable more powerful Support:
- Searching for Connections
- Filtering by Properties and Values
- even deriving new Knowledge from known Facts
Spoc-Web unifies and extends these Maps
Spoc-Web is a semantic Web and allows to create any of these Maps. In Addition to that You can design and store any Number of Representations of all Topics You ever created, because they are shared in a Database.
Adding linked Tables of quantitative Data and integrating them in to these Layouts with proper Scale is a unique Feature of Spoc-Web.
Comparison of Structure-Elements
| Structure | Mind Map | Concept Map | Topic Map | Semantic Web | Spoc-Web |
| Nodes | Theme | Concept | Topic | URI | Thing |
| Edges | Arrows | Associations | URI-Triplets | Connection | |
|
Properties |
--- | --- | --- |
Value-Triplets (Text) |
Text |
| Number | |||||
| Date | |||||
| Attachment | |||||
| Tables | --- | --- | --- | --- | Tables |
This Table shows the Techniques described above again, comparing their structural Elements. It shows how Spoc-Web surpasses other Tools and Methods due to its Completeness.